Monitor Vacuum System
Previous page: Shift Workers Documentation
In the system we have two reservoirs that we are constantly pumping, the Shells and the Fridge. The Shells is a high vacuum system and the Fridge is a 4He evaporation system operated at 1K. The pressures range expected for each apparatus are summarized in the following table.
| Apparatus | Pressure (Torr) |
|---|---|
| Shells | 10-6 - 10 -7 |
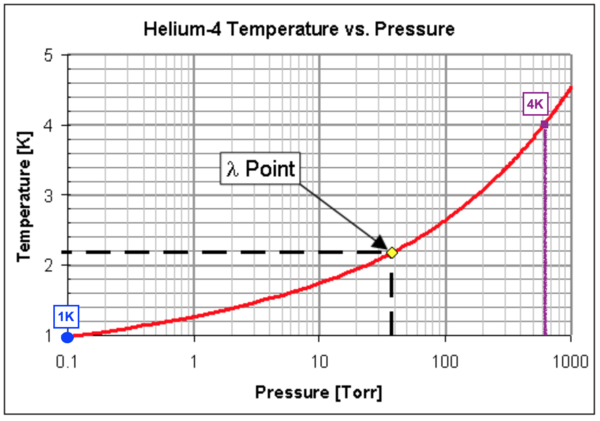
| Fridge | ~0.1 @ 1K Pressure depends on Helium4 Temperature. See Figure. |
In principle, the pressures should be stable during the cool-down but possible problems may occur and the indications of an issue are different for the shells and fridge. In the next subsections, the possible problems will be summarized along with the actions to be taken in case of a problem.
Shells
Shells pressure is obtained and maintained by a turbo pump. Keeping low pressure in the chamber is vital for the isolation of the 4K and 1K Helium of the magnet and fridge respectively. The pressure is monitored by a Ionivac ITR-090 and is recorded in the main vi. Monitoring the shells pressure over the course of the cool-down is vital to get leaks before they are unstoppable. Please monitor the pressure regularly and log any unexpected behavior. Here is a list of situations that you may encounter during the cool-down:
i. Shells pressure decreases as fridge temperature decreases: This effect is caused by the cryogenic cooling generated by the nose of the Fridge. It is normal, and it is expected that when the Fridge achieves the lowest temperature, the shells will get the minimum pressure during the cool-down.
ii. Sudden spike above 10-4Torr. This may be a symptom of a leak and here is a list of the possible causes:
- Abruptly drop in the Fridge temperature. Check the temperature of the CCS located in the shells. If the temperature changes by more than 50 degrees in less than 5 minutes the sudden cooling of the fridge may be creating an abrupt gradient of temperature in the teflon o-ring and it generates a leak. Follow the next steps:
- Close the needle valves and the roots if the are operating, only keep the roughing pumps, and wait until the pressure is recovered below 10-5Torr.
- Then, slightly open the heat exchanger valve and observe for a couple of minutes the behavior of the Pressure. Adjust the needle valve to a place you find that the cooling of the Fridge is constant and slow.
- When the temperature of the CCS in the shells reaches the temperature of the failure, proceed to normal operation of the pumps. But, continue monitoring closely in case you need to turn them off again.
- Loose pressure in the lambda point of Helium4. The lambda point of Helium4 is shown in Figure X. If the pressure of the shells is lost when the Fridge approaches the lambda point of Helium4, the presence of a cold leak in the shells is highly probable. Follow the next steps:
- Turn off the roots (in case they are on).
- Close the gate valve and needle valves. Monitor if the pressure of the shells is recovered when the Fridge exits the lambda point.
- Open the Gate valve slightly and monitor the shells while they approach the lambda point. In case the event repeats, close the gate valve and repeat again, the steps above. If the temperature in the Fridge continues increasing, it means that you possibly lost all the Helium4 in the Fridge. Therefore, open slightly(how much?) the needle valves.
- If you confirm the presence of a cold leak the physics goals of the cool-down may change and you need to consult your shift leader. While she/he redirect the course of the cool-down, don’t allow the Fridge to warm. Therefore, the steps of opening and closing the gate valve/needle valves need to be repeated constantly until the goals of the cool-down are reset.
- Roughing pump failed: If there is an abrupt oil spill of the pump and/or it does not restart. Solution: Replace the pump with a spare roughing pump.
- Turbo Pump failed: If the pressure goes abruptly above 10-3Torr the Turbo will shut-off automatically by its safety system. And, failure of the pump may not be very obvious , but if the shell's pressure was stable as well as the temperature along the different temperature sensors of the Fridge (Check all the temperatures of the fridge during the past ~20 minutes of the event), a turbo pump failure may be the cause. If the pressure is maintained of the order of 80 mTorr or below by the roughing pump attempt to restart the turbo pump and see if the temperature decreases to at least 10-5Torr in a couple of minutes. If it does, the turbo pump may be OK and monitor all the other systems to find the cause and/or prevent a repetition of the event. But, if it does not restart, please change the turbo with a spare.
Fridge
The Fridge pressure is related with the temperature of the nose when the temperature is below 4K, as shown in Figure X. It is very difficult to detect Fridge leaks during normal operation of the Fridge but here is a list of things you need to check regularly during the cool-down:
- During/After a target swap: Make sure the o-rings of the Piston are adequate. Be careful in the insert/extract of the target stick. If the o-rings are compromised after the extraction of the sticks, change them by new ones. Piston o-rings can be found in the red buckets on the wall near to the roots.
- Moving the microwaves/target stick: Since the mechanism for moving the microwaves/target stick changes the sealing that keep vacuum on the Fridge. Always make sure that you do those slow and careful. The rule to follow is that after any movement, the fridge should return to its operation status. Therefore do changes one by one and wait until the Fridge recovers to its previous state to make any other change.
Never let the Fridge go above 30K. Always check that all the pressure systems (Fridge and Magnet) have pop-off valves and they are unfrozen and working to avoid any possible over-pressure (Creating a bomb).