Postfix
Postfix is a mail transfer agent that routes and delivers e-mail.
Diagnosis
What you can do to check if postfix is working.
- Send yourself a message from a Gmail account.
- Mtools: https://mxtoolbox.com/SuperTool.aspx?action=smtp%3aeinstein.unh.edu&run=toolpage#
- Ultra Tools: https://www.ultratools.com/tools/emailTest
- Check the Blacklists: https://mxtoolbox.com/blacklists.aspx or http://mail-blacklist-checker.online-domain-tools.com
- Try to telnet to einstein.unh.edu port 25.
- Note that this does not mean postfix is actually working properly, but if this doesn’t nothing else will.
- Contact Bryan Scoville <Bryan.Scovill@unh.edu> at UNH Telecom and ask to check the network connections.
Centos 7 Postfix
We upgraded Einstein to Centos 7 and a newer version of postfix.
OUTDATED OLD POSTFIX
Configuration
Postfix stores its configuration files in the /etc/postfix/ directory. The following is a list of the more commonly used files:
- access
- Used for access control, this file specifies which hosts are allowed to connect to Postfix. Empty, except for comment documentation
- aliases
- A configurable list required by the mail protocol. Not present
- main.cf
- The global Postfix configuration file. The majority of configuration options are specified in this file.
- master.cf
- Specifies how Postfix interacts with various processes to accomplish mail delivery.
- transport
- Maps email addresses to relay hosts. Has one significant line:
xemed.com smtp:gm.xemed.com
Basic Postfix Configuration
Make sure that you use the system-switch-mail or system-switch-mail-gnome program to select Postfix as the default MTA. If you don't, you'll thrash the mail system and lose mail!
Standard Postfix Configuration
Slightly more advanced configuration: README
From RedHat:
By default, Postfix does not accept network connections from any host other than the local host. Perform the following steps as root to enable mail delivery for other hosts on the network:
- Edit the /etc/postfix/main.cf file with a text editor, such as vi.
- Uncomment the mydomain line by removing the hash mark (#), and replace domain.tld with the domain the mail server is servicing, such as example.com.
- Uncomment the myorigin = $mydomain line.
- Uncomment the myhostname line, and replace host.domain.tld with the hostname for the machine.
- Uncomment the mydestination = $myhostname, localhost.$mydomain line.
- Uncomment the mynetworks line, and replace 168.100.189.0/28 with a valid network setting for hosts that can connect to the server.
- Uncomment the inet_interfaces = all line.
- Restart the postfix service.
Once these steps are complete, the host accepts outside emails for delivery.
However, much of this is actually unnecessary since Postfix has intellegent defaults (e.g. it can figure out the machine's hostname automatically). Follow the Postfix readme instead.
Database Configuration
Setting up Postfix to cooperate with LDAP: README
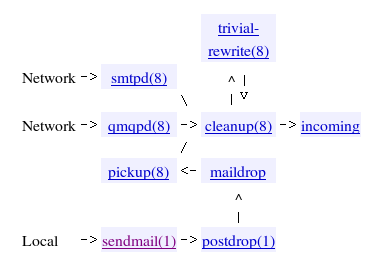
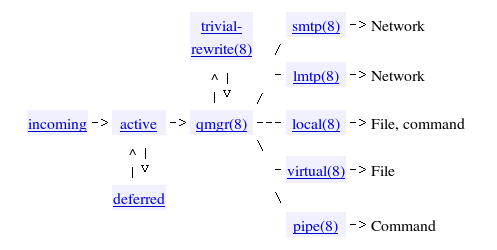
Postfix Architecture Overview
How Postfix recieves mail
We use smtpd. Yes, our "sendmail" isn't the real thing, but rather a Postfix component.