Difference between revisions of "Kvm"
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
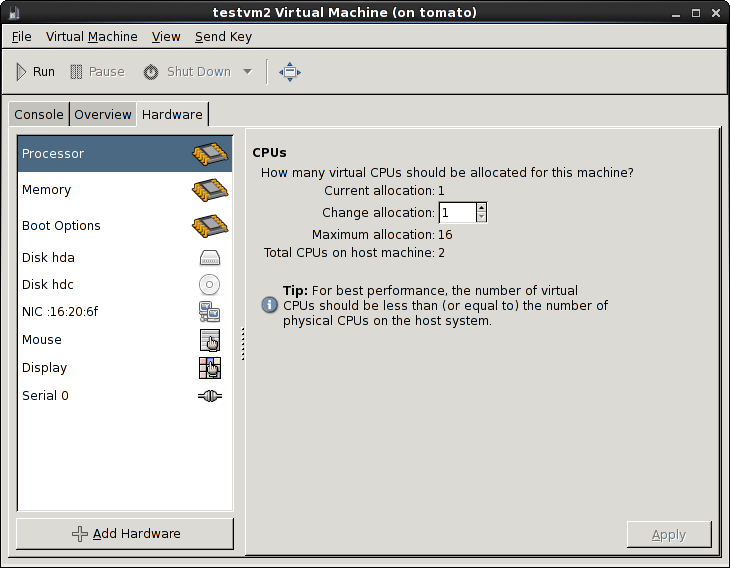
[[Image:kvm-hardware-view.png|The virt-manager hardware interface]] | [[Image:kvm-hardware-view.png|The virt-manager hardware interface]] | ||
| − | [[Image:kvm-console.png|CentOS booting in the virt-manager console]] | + | [[Image:kvm-console.png|500px|thumb|CentOS booting in the virt-manager console]] |
Revision as of 21:10, 11 December 2011
KVM is a Linux-based full virtualization tool which utilizes the virutalization extensions available with several models of Intel and AMD processors.
Installation
Prerequisites
KVM will only work on systems with processors offer virtualization support. To find out if a system's processor supports virtualization you can look in /proc/cpuinfo for the vmx (Intel) or svm (AMD) flags. This command should do the trick:
egrep '(vmx|svm)' --color=always /proc/cpuinfo
NPG Systems With Virtualization Support
Installing the Software
If you're using a RHEL system you need to enable the virtualization add-on entitlement to your RHEL license. You can install the packages via yum. This is the list of packages you will need:
libvirt-python kvm virt-manager libvirt kvm-qemu-img kmod-kvm kvm-tools python-virtinst
Configuration
Start the libvirtd service, and configure it to start at boot.
chkconfig --level 345 libvirtd on service libvirtd start
Network Bridging
KVM requires bridged networks to be configured manually. The configuration for RHEL 5 systems should look something like this:
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE=eth0 ONBOOT=yes HWADDR=FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF BRIDGE=br0
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-br0
ONBOOT=yes TYPE=Bridge DEVICE=br0 BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR=10.0.0.2 NETMASK=255.0.0.0 NM_CONTROLLED=no DELAY=0
Also, the system firewall should contain a rule that forwards traffic to the bridged interfaces. This will require virtual systems to maintain their own firewalls because it won't be filtered by the host:
-I FORWARD -m physdev --physdev-is-bridge -j ACCEPT
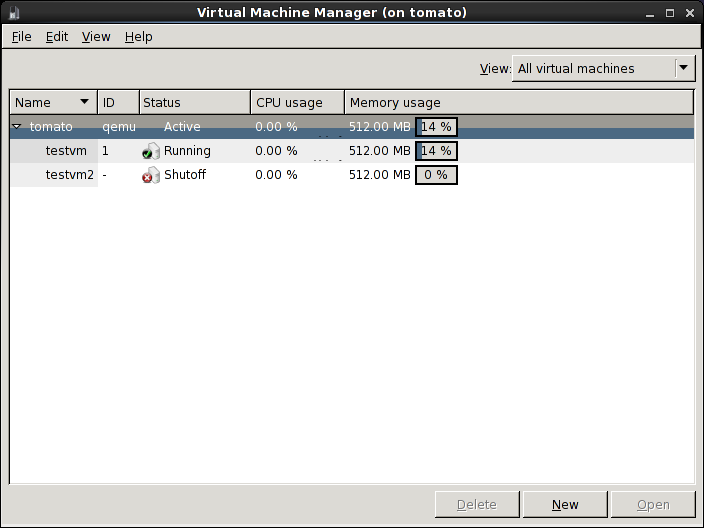
Managing Virtual Machines
The virt-manager tool provides a GUI for creating and managing VMs.
virt-manager can be used to view virtual machine details, add and remove virtual hardware, and access the system console.